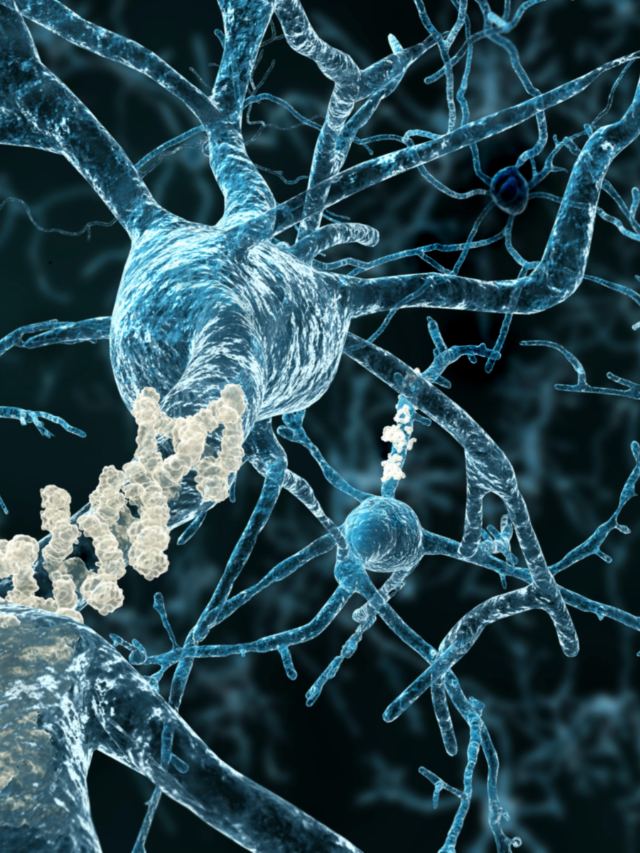
Alzheimer's is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting memory and reasoning.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
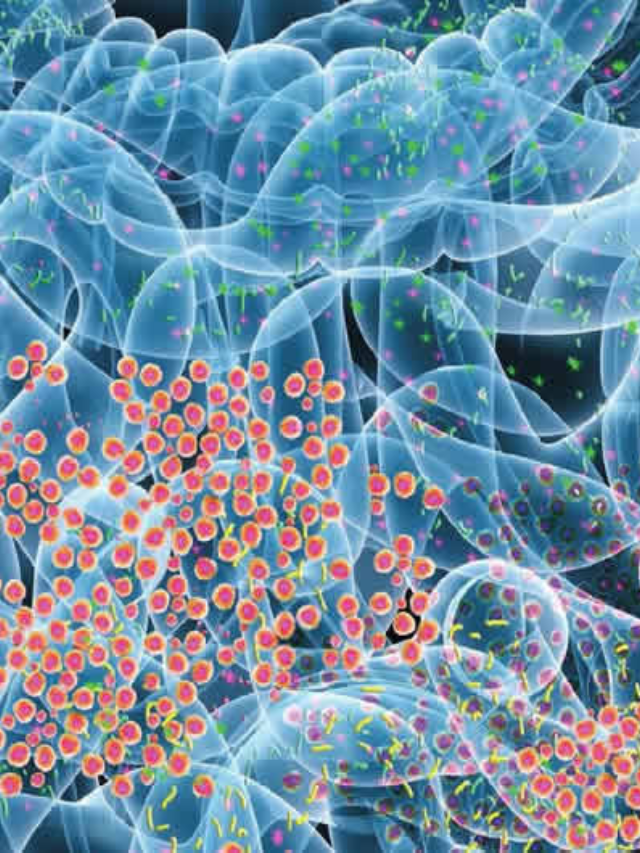
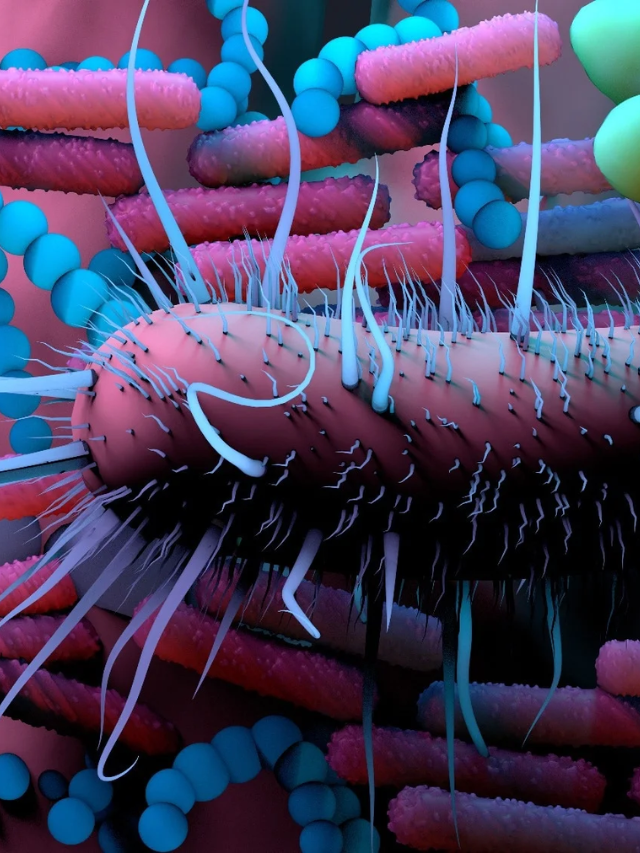
Previous research shows gut bacteria changes occur in Alzheimer's patients.
Gut Bacteria and Alzheimer’s

Researchers used AI, genetics, and multi-omics analysis to explore gut bacteria metabolite interactions with human receptors.
AI Unveils Gut-Brain Connection

Machine learning analyzed over a million metabolite-receptor pairs to predict interactions relevant to Alzheimer's.
AI Predicts Key Gut-Brain Interactions
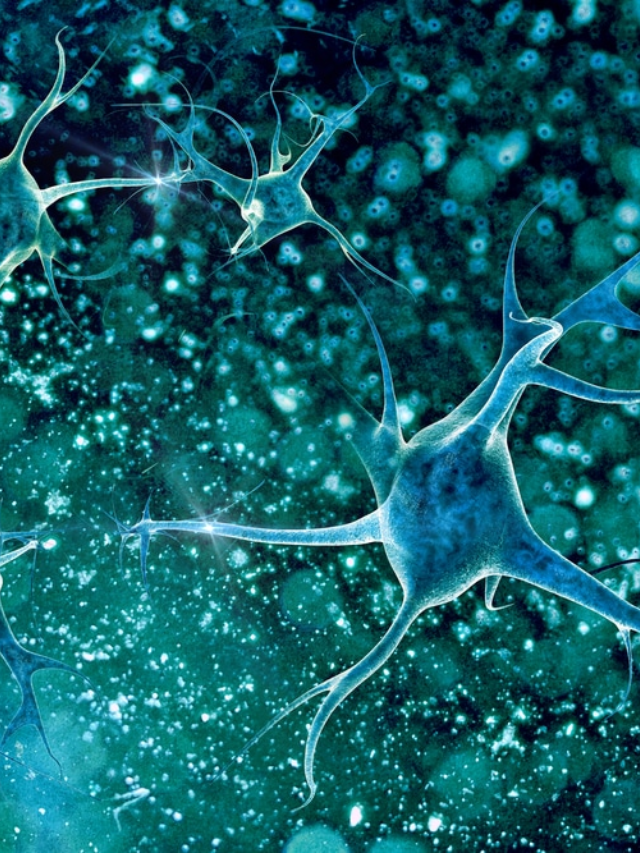
The study identified G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that interact with gut bacteria metabolites.
New Targets for Drug Development

The research highlighted phenethylamine and agmatine for their effects on tau proteins, a key marker of Alzheimer's progression.
Phenethylamine and Agmatine
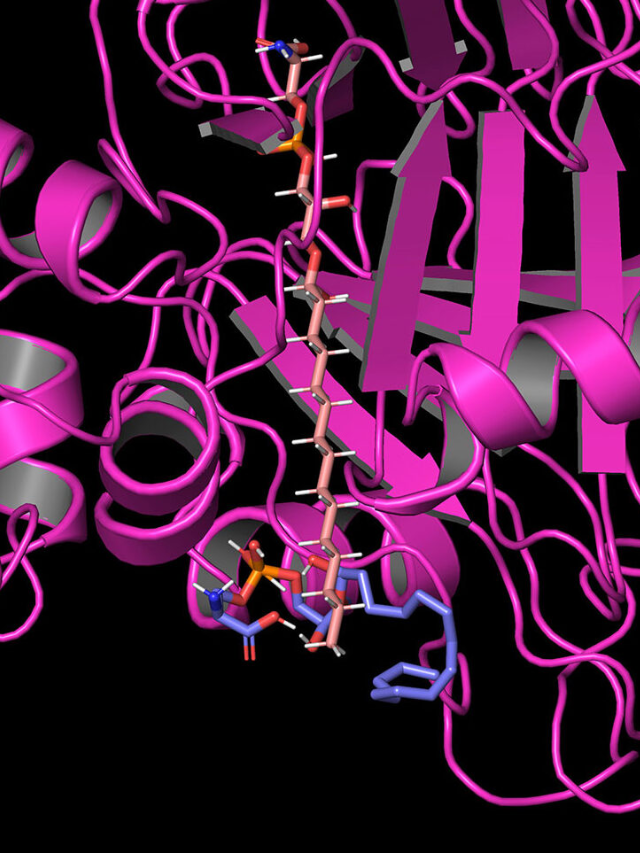
Combining AI, genetics, and experimental validation strengthened the study's findings.
The Power of Multifaceted Research
The study lays the groundwork for future research to validate findings in living organisms.